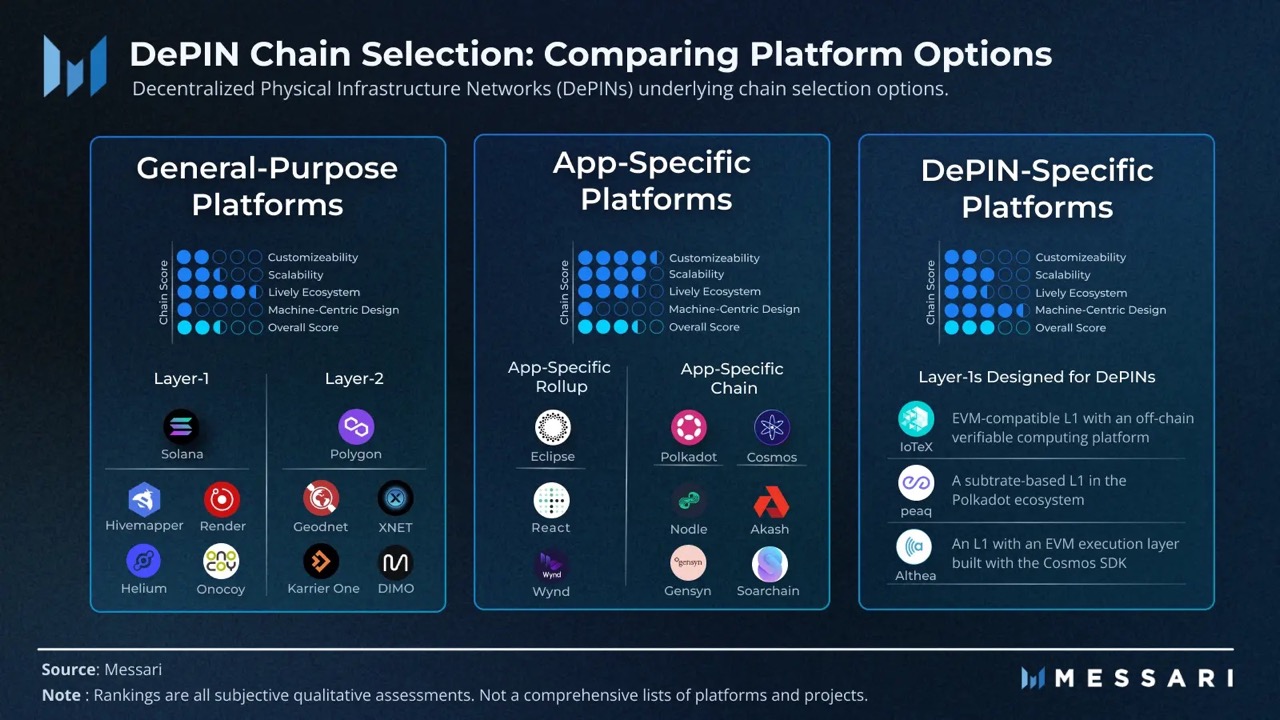
The fusion of blockchain and the real world, where anyone can own, share, and profit from physical infrastructure in a decentralized way. Let’s deep dive in DePIN.
The decentralized finance market is evolving at a lightning-fast pace, but we’re still in the very early stages. According to Binance research, less than 1% of the global population uses Web3.
At this rate, mass adoption seems far off. But let’s close our eyes for a moment and imagine an ideal world—a world without annoying intermediaries, where purchasing any product or service takes just a few clicks and a transaction signature. A world where infrastructure is managed by communities, via DAOs, and every proposal is voted on openly.
At first glance this may seem utopian, but this is exactly the kind of change that one of the most technologically advanced narratives in DeFi – DePIN – will introduce to our lives.
What is DePIN?
Source: Messari
Once upon a time in the world of blockchain, a visionary project called Helium was born with a simple yet revolutionary idea: what if everyday people could build a global wireless network? It all began in 2013, when a group of forward-thinking entrepreneurs realized that the centralized telecom giants controlled the airwaves, stifling innovation and limiting access.
Helium set out on a bold mission to change that, harnessing the power of blockchain technology and the concept of DePIN—Decentralized Physical Infrastructure Networks. They imagined a world where anyone could set up a small device, called a hotspot, in their home or office, and in return, earn cryptocurrency for providing wireless coverage to their neighbors.
As more and more people joined the Helium network, what started as a small ripple grew into a tidal wave of decentralized connectivity, forming a grassroots-driven global 5G network. This tale of Helium is not just about technology; it’s a story of how the power of community can reshape entire industries, proving that sometimes the most impactful revolutions begin with the simplest of ideas.
As Helium’s network grew, so did its impact. What started as a few enthusiasts setting up hotspots in their homes has now become a sprawling global network with thousands of nodes across the world. Helium’s decentralized wireless network, once just a bold idea, has surpassed 100,000 users, offering affordable 5G coverage at a fraction of the cost compared to traditional providers. Today, Helium stands as a shining example of what’s possible when the power of blockchain and community come together—transforming not just technology, but the way we connect with each other in a more open, decentralized world.
DePIN (Decentralized Physical Infrastructure Networks) represents decentralized networks that use distributed ledger technology and tokenization to create and manage physical and digital infrastructures. This concept introduces a new approach to traditional business, allowing organizations to launch, expand, and incentivize their users independently, without relying on initial capital or being controlled by large corporations or governments.
Traditionally, critical infrastructure, like power grids or the Internet, is managed centrally by governments or major corporations. “Big Brother is watching you,” as they say.

But the main goal of DePIN is to shift this paradigm, handing back control and ownership of infrastructure to the community. This shift is the crypto narrative that could significantly change our lives, making them freer and more decentralized.
How Does DePIN Work?
DePIN relies on five key components to create and maintain infrastructure: Decentralization, Blockchain, Smart Contracts, Tokenization, and Security.
Decentralization means there is no central authority. Even if you wanted to, you couldn’t find a central entity that makes decisions alone within a DePIN system. Instead, there’s a protocol for network communication and interaction between node runners and validators.
Blockchain is the foundational component for creating a decentralized ecosystem. It ensures transparency and immutability within the architecture. Blockchain is the technical enabler that makes DePIN possible.
Smart Contracts provide the logic that ensures a programmable organizational structure and project functionality.
Tokenization involves creating a native token that not only represents physical and digital artifacts within the ecosystem but also serves as rewards for active participants.
Security is a fundamental requirement to protect the integrity and confidentiality of information. Before launching on the mainnet, every project undergoes rigorous and comprehensive audits.
DePIN Flywheel
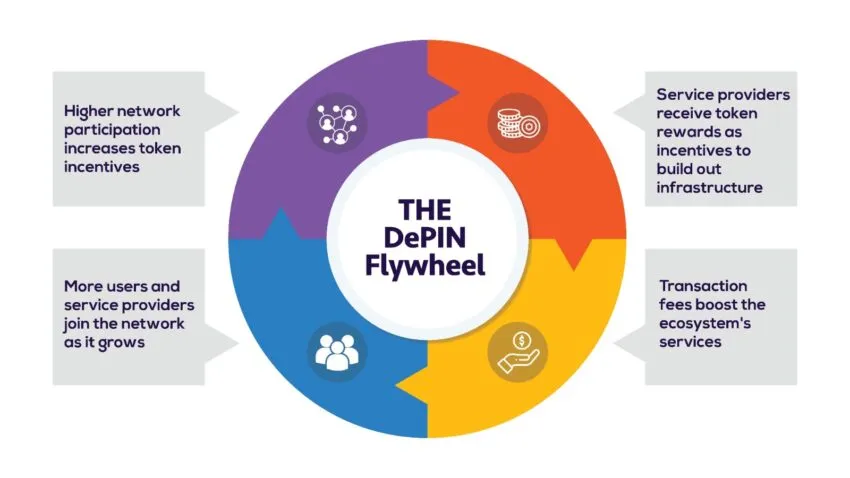
For those thinking about creating their own DePIN project, a special DePIN Flywheel has been developed, illustrating the development process of DePIN projects:
Red: Most projects start by motivating service providers to participate actively. They are incentivized with native tokens, rewards points, or revenue-sharing agreements.
Yellow: Motivated participants begin actively using the project’s features, increasing overall metrics like TVL and Volume. Service providers start earning transaction fees, which gets the flywheel spinning.
Blue: As the project grows, more users and service providers join, further accelerating the flywheel.
Purple: Ultimately, this increases project activity, allowing for even greater rewards for service providers, which improves service quality. This leads to further project growth and strengthens its position.
Types of DePIN
DePIN can be divided into two main types: Physical Resource Networks (PRN) and Digital Resource Networks (DRN).
Physical Resource Networks (PRN): These are decentralized networks of physical resources like equipment, mobility, and energy. These resources are tied to specific locations and can’t be easily transferred.
Digital Resource Networks (DRN): These include providers of digital resources like computing power, bandwidth, and storage. These resources are not tied to specific locations.
DePIN Categories
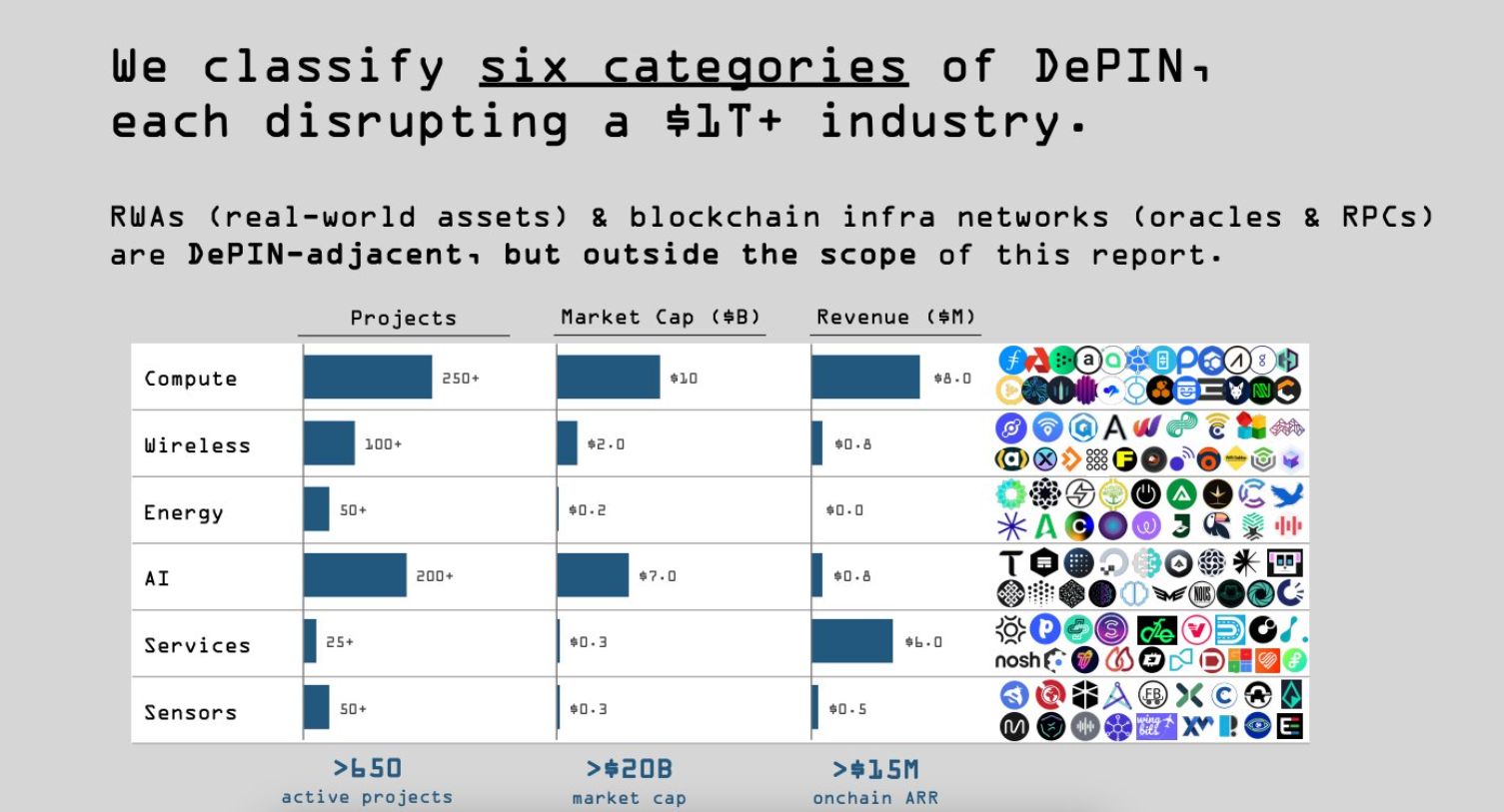
Based on the Messari report, DePIN projects can be divided into six categories:
1) Compute
This category is associated with online computing, where computers and other devices provide shared resources, software, information, or storage space. Currently, a large amount of computing power is wasted, despite high demand. DePIN addresses this problem by acting as a marketplace where hardware owners can offer their computing power to users who need it.
- Render Network: A decentralized platform for cloud computing, offering scalable and cost-effective infrastructure for developers and enterprises. Essentially, Render creates a P2P market for interaction between:
- User A, who needs rendering services and is willing to pay for them.
- Users B, who have unused capacities in the form of idle GPUs.
- User A assigns a task, and User B completes it, receiving payment in $RENDER tokens.
- Filecoin: A decentralized storage network designed to store humanity’s most important information. Similar to Render, Filecoin allows renting out unused gigabytes on hard drives in a P2P network.
- Spheron Network – Decentralised GPU Marketplace;
2) Wireless
This category is related to wireless networks. DePIN offers a decentralized approach to bridging the connectivity gap. Participants in projects contributing to the expansion of wireless network coverage, whether by hosting nodes or enhancing network security, are rewarded. This not only fosters the growth of a reliable and extensive wireless network but also empowers local communities to shape their digital connectivity landscape.
- Since its launch in December 2023, Helium Mobile offers wireless coverage for $20 a month compared to a $144 national average. The service had already surpassed 100,000 users, validating the narrative of decentralized 5G.
3) Energy
This category is related to the energy sector, aimed at promoting the production of “green” energy by establishing connections between renewable energy providers and companies using these energy sources. These projects contribute to the collection of reliable energy supply data and the use of this data to develop environmentally friendly energy consumption methods.
- Arkreen: This project incentivizes green energy providers to supply data about their energy installations. The data provided includes the capacity of solar installations and similar data. The demand for such an application includes issuers of Renewable Energy Certificates (RECs) and green computing operators who access energy data and create applications and services based on this data.
4) AI
This category is associated with artificial intelligence, focused on distributing GPU capacities, AI agents, and training LLM models on-chain, with the possibility of using zero-knowledge technology.
- ChainGPT – is an advanced AI model that assists individuals and businesses;
5) Services
A category associated with both physical and digital resource networks, essentially consisting of Web2 project analogs but on the blockchain.
- Teleport: A decentralized aggregator of taxi services.
6) Sensors
This category is related to devices that detect and measure physical data from the environment, such as temperature, pressure, light, sound, or movement, and convert it into a signal that can be interpreted by a machine or human. Sensor data is useful when considering a network of sensors located in different places, as it makes the information more reliable. Additionally, these sensors can interact with each other and assist in forecasting, such as climate prediction.
- IOTA: An open-source distributed ledger built for the Internet of Things.
However, several more categories have recently emerged that can be added to this list:
7) Decentralized Generative Energy (DeGEN)
The projects from this category are building virtual power plants to modernize the energy grid and incentivize the deployment of solar farms to reduce global CO2 emissions.
- Star Powerworld: An energy network that connects energy equipment to empower applications like Virtual Power Plants and Carbon Credit systems.
- SRCFUL: The first blockchain-powered Virtual Power Plant in the Helium ecosystem. Unlocking Distributed Energy Resources.
8) Decentralized Gaming Infrastructure (DeGIN)
The boom in GPU computing networks has led to a new use case in “pixel streaming”. Pixel streaming allows high-end gaming computers to stream graphically intensive games to lower-end computers and other devices. To scale large, content-rich virtual games for millions of simultaneous players, persistent objects and AI, the industry needs new solutions to old problems. GPU networks can enable pixel streaming at a lower cost by allowing gaming computers to sell their excess GPU processing power to the network.
- Aethir Cloud: Scalable Decentralized Cloud Infrastructure (DCI) for Gaming & AI.
9) Zero-knowledge Transport Layer Security (zkTLS)
zkTLS enables verifiable attestation of data to a third party. This opens up all of Web2 to “vampire attacks,” enabling DePIN protocols to break Web2 incumbent moats.
- Opacity Network: It solves this using a three-part construction that involves a key-upgrade mechanism.
Advantages & Disadvantages of DePIN
Compared to traditional infrastructure, DePIN has several advantages:
- Capital attraction through crowdfunding and token incentives.
- Blockchain settlements, making such systems transparent and fair.
- Elimination of single points of failure, avoiding heavy loads on cloud and other servers.
- Experimental approach and improved process automation.
However, DePIN also has several disadvantages:
- The risk of programming errors in smart contracts, which can lead to fatal consequences for the system.
- High volatility of the crypto market can negatively affect the value of tokens in which DePIN project participants receive rewards.
- DePIN projects may face regulatory scrutiny, which could slow down the mass adoption of this narrative.
- Connecting to a DePIN project can be challenging for newcomers.
The Future of DePIN
In the near future, several new subsectors may dominate the DePIN sector:
- ZK-verifiable cloud GPUs: This will create a new decentralized economy based on AI.
- Decentralized AI services available to users.
- Memecoins with utilities based on DePIN.
DePIN helps reduce network load, create more adaptable infrastructure, expand capacity, and decentralization. They also allow for the introduction of innovative technologies in regions where centralized structures have limitations. In the future, DePIN will provide people with access to rewards for using familiar things like WiFi and transportation. The technology is in growing demand and has many prospects.
Conclusion
Although the DePIN narrative may not be the most popular in the crypto community, it is certainly at the forefront of innovation, and right now, dozens of innovative projects are being created at the intersection of blockchain and AI, which will change our lives.
The move towards a more decentralized, secure, and efficient world is not only possible but is already happening, promising a future where technology enables everyone to contribute to a collective, interconnected network and benefit from it.
With the right circumstances and proper development, DePIN will undoubtedly change our daily lives for the better. The community will have the opportunity to create and manage infrastructure projects on a decentralized, fair, and sustainable basis.
READ MORE: